Neo4j is a great graph database that is easy to get started with, and provides an excellent tool to test queries and visualize the data structure using Neo4j Desktop.
In this article, I will guide you through the process of setting up a dev environment where you connect to the Neo4j DBMS, and run queries using Python.
Env setup
Before you can do enything you should set up a virtual environment where you can install all your dependencies.
python3 -m venv venv
chmod u+x venv/bin/activate
source venv/bin/activateThen you must install the Neo4j package, and the dotenv package. To make things simple, create this file:
vim requirements.txtneo4j
python-dotenvThen install the packages defined in this file:
pip install -r requirements.txtFinally, add env variables to the .env file
vim .envNEO4J_URI="bolt://localhost:7687"
NEO4J_USER=your_db_user
NEO4J_PASSWORD=your_db_passwordPlease note that you must use the bolt protocol when connecting to a single Neo4j instance. Bolt is the application protocol used for executing CQL (Cypher Query Language).
WSL Considerations
Windows Subsystem for Linux setup
If you run your dev environment in WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), you must perform additional setup. Technically, WSL is not your local host where you have Neo4j Desktop is running, so you must allow incoming connections to the Neo4j instance.
To allow for remote connections, open Neo4j desktop, navigate to Local Instances, and click on the three dots in the top-right --> Open --> Instance Folder. Then open the conf directory where you find the neo4j.conf file. Open this file in a text editor.
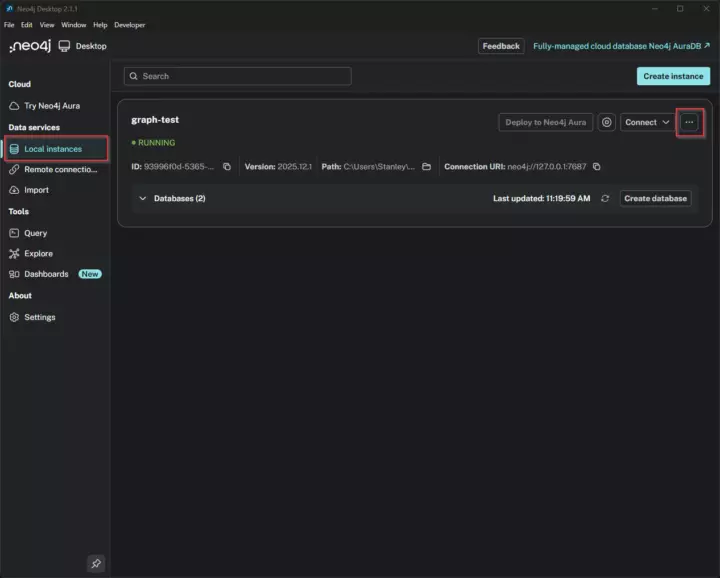
Local instances
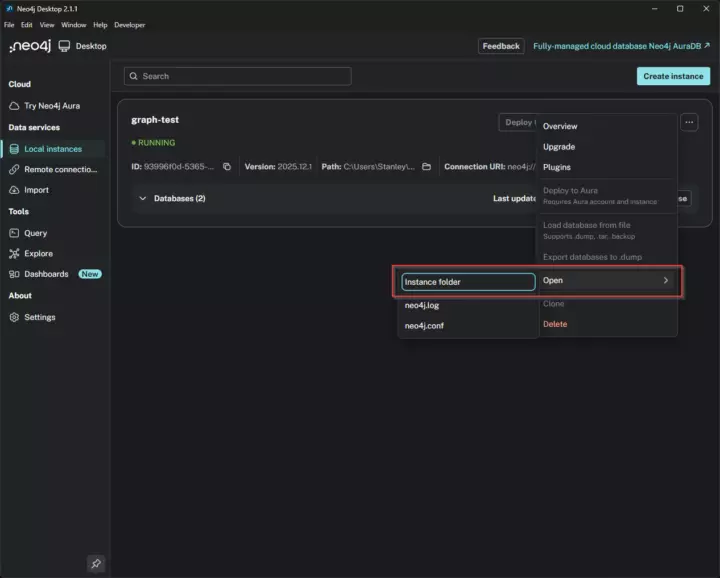
Open Instance Folder
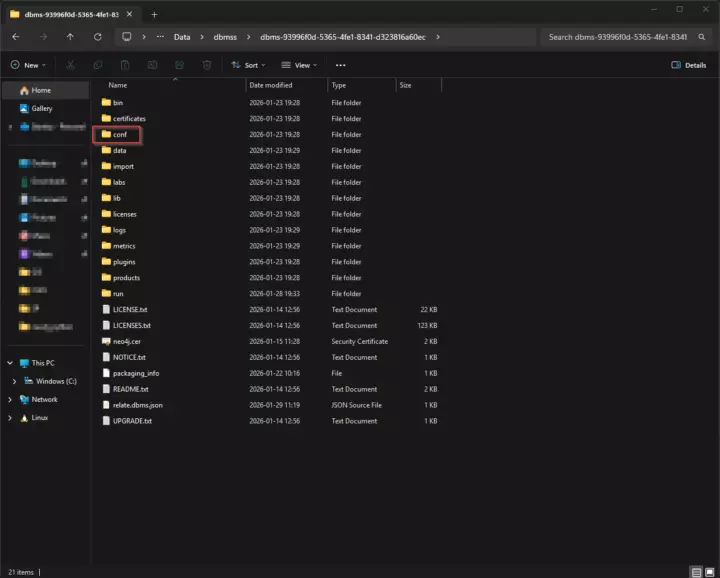
Open conf directory
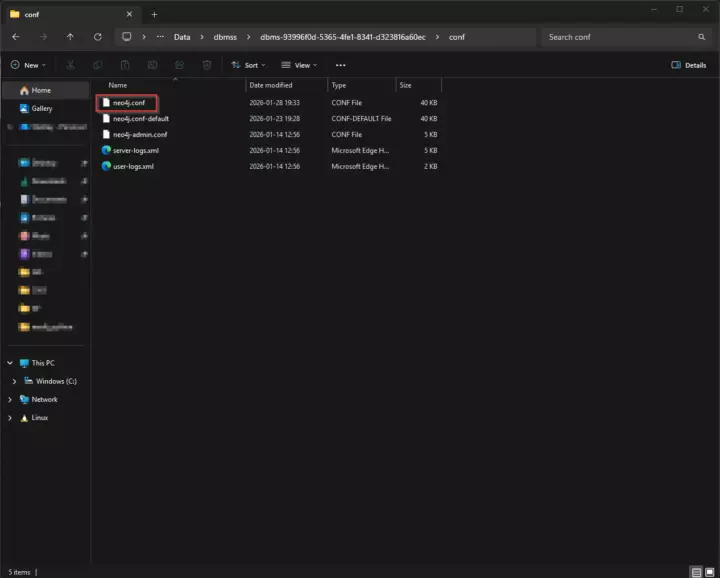
Open the neo4j.conf file in a text editor
Search for and uncomment (remove the # symbol at the beginning) the line that says "server.default_listen_address=0.0.0.0".
...
#*****************************************************************
# Network connector configuration
#*****************************************************************
# With default configuration Neo4j only accepts local connections.
# Use 0.0.0.0 to bind to all network interfaces on the machine. If you want to only use a specific interface
# (such as a private IP address on AWS, for example) then use that IP address instead.
server.default_listen_address=0.0.0.0
...Save the changes, and restart the Neo4j instance by stopping it and starting it again. When the instance starts, you must accept the Java application to make changes to your computer. This will allow you to connect to the Neo4j instance from WSL.
To get the IP of your host machine (Windows) from WSL, run this command:
ip route show | grep -i default | awk '{ print $3}'
172.27.176.1In the example above, my IP address was 172.27.176.1.
To test the connection to your Neo4j instance, run the command below. Replace my IP with yours.
nc -zv 172.27.176.1 7687
Connection to 172.27.176.1 7687 port [tcp/*] succeeded!If the connection was successfull, you can update your .env file accordingly
vim .envNEO4J_URI="bolt://172.27.176.1:7687"
NEO4J_USER=your_db_user
NEO4J_PASSWORD=your_db_passwordBase Class + Test
To test the connection to Neo4j, which has the basic functionality, create this file:
vim Neo4jHandler.pyfrom neo4j import GraphDatabase
class Neo4jHandler:
def __init__(self, uri, user, password):
try:
auth = (user, password)
self.driver = GraphDatabase.driver(uri, auth=auth)
self.driver.verify_connectivity()
print("Successfully connected to Neo4j!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: Failed to create the Neo4j driver: {e}")
self.driver = None
def close(self):
if self.driver:
self.driver.close()To test the connectivity, create a new file:
vim connectionTest.pyimport os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from Neo4jHandler import Neo4jHandler
if __name__ == "__main__":
load_dotenv()
URI = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI")
USER = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER")
PASSWORD = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
neo4j_handler = Neo4jHandler(URI, USER, PASSWORD)
neo4j_handler.close()Test the connection by running this script.
python3 connectionTest.py
Successfully connected to Neo4jCreate Nodes
Creating nodes is as simple as running Cypher queries in Neo4j Desktop. To make it easy to run queries in Python, you can extend the class we created in the previous chapter.
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from Neo4jHandler import Neo4jHandler
class Neo4jHandlerCustom(Neo4jHandler):
def create_node(self, name, age, email):
if not self.driver:
print("Driver not initialized.")
return
with self.driver.session() as session:
session.run(
"CREATE (p:Person {name: $name, age: $age, email: $email})",
name=name,
age=age,
email=email
)
print(f"Node created: {name}, {age}, {email}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
load_dotenv()
URI = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI")
USER = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER")
PASSWORD = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
neo4j_handler = Neo4jHandlerCustom(URI, USER, PASSWORD)
neo4j_handler.create_node("Alice Johnson", 30, "alice.johnson@example.com")
neo4j_handler.create_node("Bob Smith", 30, "bob.smith@example.com")
neo4j_handler.create_node("Charlie Brown", 30, "charlie.brown@example.com")
neo4j_handler.close()Running this script will create three Person nodes that have the attributes name, age, and email.
python3 createNodesSimple.py
Successfully connected to Neo4j
Node created: Alice Johnson, 30, alice.johnson@example.com
Node created: Bob Smith, 30, bob.smith@example.com
Node created: Charlie Brown, 30, charlie.brown@example.comCreate Edges
Using CQL, it's easy to add relationship-based selection parameters.
Add the following method the the Neo4jHandlerCustom class:
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from Neo4jHandler import Neo4jHandler
class Neo4jHandlerCustom(Neo4jHandler):
def create_relationships(self, name1, name2):
if not self.driver:
print("Driver not initialized.")
return
with self.driver.session() as session:
session.run(
"""
MATCH (a:Person {name: $name1}), (b:Person {name: $name2})
CREATE (a)-[:FRIEND_WITH]->(b)
CREATE (a)<-[:FRIEND_WITH]-(b)
""",
name1=name1,
name2=name2
)
print(f"Created a two-way relationship FRIEND_WITH between {name1} and {name2}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
load_dotenv()
URI = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI")
USER = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER")
PASSWORD = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
neo4j_handler = Neo4jHandlerCustom(URI, USER, PASSWORD)
neo4j_handler.create_relationship("Alice Johnson", "Bob Smith")
neo4j_handler.create_relationship("Alice Johnson", "Charlie Brown")
neo4j_handler.close()Running this script will create a bidirectional relationship between the persons.
python3 addFriendEdge.py
Successfully connected to Neo4j!
Created a two-way relationship FRIEND_WITH between Alice Johnson and Bob SmithGet Nodes with a specific Edge
Using CQL, it's easy to make relational queries based on Edge type.
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from Neo4jHandler import Neo4jHandler
class Neo4jHandlerCustom(Neo4jHandler):
def find_person_with_friends(self):
if not self.driver:
print("Driver not initialized.")
return
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(
"""
MATCH (a:Person)-[:FRIEND_WITH]->(b:Person)
RETURN a AS person1, b AS person2
"""
)
for record in result:
print(f"{record['person1']} is friends with {record['person2']}")
def find_two_way_friends(self):
if not self.driver:
print("Driver not initialized.")
return
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(
"""
MATCH (a:Person)-[:FRIEND_WITH]->(b:Person)
WHERE (b)-[:FRIEND_WITH]->(a)
AND elementId(a) < elementId(b)
RETURN a AS person1, b AS person2
"""
)
for record in result:
print(f"{record['person1']['name']} and {record['person2']['name']} are two-way friends")
def find_persons_friends(self, name):
if not self.driver:
print("Driver not initialized.")
return
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(
"""
MATCH (p:Person {name: $name})-[:FRIEND_WITH]->(f:Person)
RETURN f
""",
name=name
)
print(f"Friends of {name}:", end=" ")
print(", ".join([record['f']['name'] for record in result]))
if __name__ == "__main__":
load_dotenv()
URI = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI")
USER = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER")
PASSWORD = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
neo4j_handler = Neo4jHandlerCustom(URI, USER, PASSWORD)
print("-----")
neo4j_handler.find_person_with_friends()
print("-----")
neo4j_handler.find_two_way_friends()
print("-----")
neo4j_handler.find_persons_friends("Alice Johnson")
neo4j_handler.close()python3 getPersonsWithFriends.py
Successfully connected to Neo4j!
-----
Alice Johnson is friends with Bob Smith
Alice Johnson is friends with Charlie Brown
Bob Smith is friends with Alice Johnson
Charlie Brown is friends with Alice Johnson
-----
Alice Johnson and Bob Smith are two-way friends
Alice Johnson and Charlie Brown are two-way friends
-----
Friends of Alice Johnson: Bob Smith, Charlie BrownThe find_person_with_friends() method will print all nodes that have a the ralationship with another person.
The find_two_way_friends() method will print pairs that have a two-way relationship.
The find_persons_friends() prints all friends of a person.
Congratulations, you now have an overview of the most basic ways of using Neo4j with Python 🎉